


For this diagnosis to be made, the ECG must show ST-segment elevation of at least 0.1 mV (1 mm) in two consecutive leads. ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI) is most commonly caused by acute rupture of atherosclerotic plaque and thrombosis of the involved coronary arteries. The arrangement of the leads produces the following anatomical relationships: leads II, III, and aVF view the inferior surface of the heart leads V1 to V4 view the anterior surface leads I, aVL, V5, and V6 view the lateral surface and leads V1 and aVR look through the right atrium directly into the cavity of the. In the presence of persistent ST elevation in anterior chest leads, the R in aVR is suggestive of left ventricular aneurysm (Goldburger's sign).įor example, leads V3 and V4 are contiguous V1 and V2 are also contiguous aVL and I are also contiguous V3 and V5 are not contiguous, because lead V4 is placed between these leads. In pericarditis, lead aVR is most often the only lead which shows reciprocal ST depression where as in Acute Infarction, usually a group of leads shows reciprocal depression. aVF means augmented Vector Foot the positive electrode is on the foot. aVL means augmented Vector Left the positive electrode is on the left shoulder.
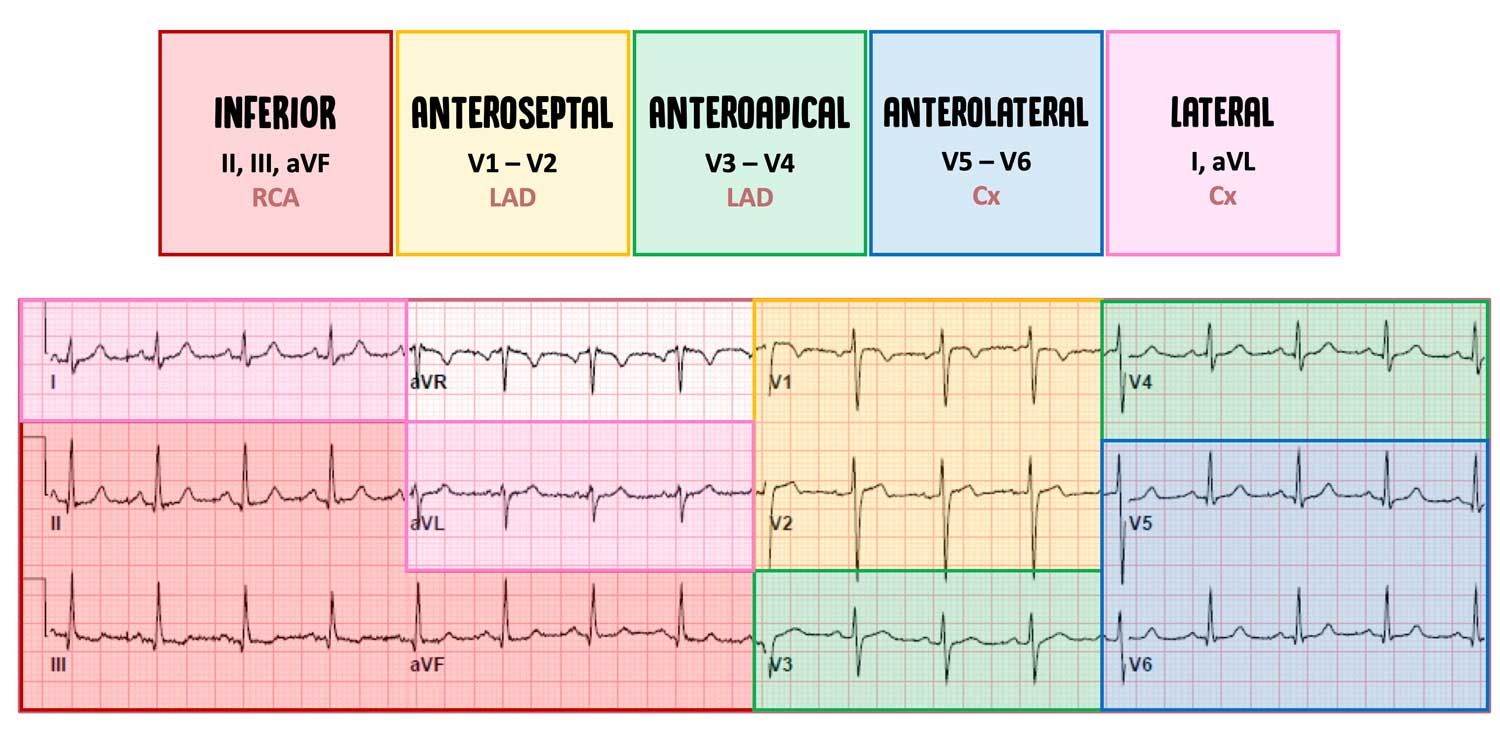
The importance of multiple leads is illustrated in the diagnosis of myocardial infarction (MI).ĪVR means augmented Vector Right the positive electrode is on the right shoulder. To a certain extent, the more points that are recorded, the more accurate the representation of the heart's electrical activity. Reciprocal change is defined as ST-segment depression occurring on an ECG which also has ST-segment elevation in at least 2 leads in a single anatomic segment.Jun 20, 2014 Reciprocal change is a very important ECG finding, not only supporting the diagnosis of STEMI but also indicating a high-risk patient. You should know what contiguous leads are before attempting to interpret a 12-Lead ECG.Ĭontiguous leads Picture EKG Lead Lateral I, aVL, V5, V6 Inferior II, III, aVF Septal V1, V2 Anterior V3, V4 Inverted waves aVR Axis Deviation Look at lead I and aVF I- If deflects up its left aVF- If deflects up its down Normal Axis Deviation I- Up aVF- Up Left Axis Deviation I- Up aVF- Down Right Axis Deviation I- Down aVF- Upġ:259:44What are contiguous leads? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo all of those leads are considered contiguous to each other it leads one AVL will be 5 and b6.MoreSo all of those leads are considered contiguous to each other it leads one AVL will be 5 and b6.Įlectrocardiogram LeadsLimb Leads (Bipolar)Augmented Limb Leads (Unipolar)Chest Leads (Unipolar).For example, these states in the upper-midwest are contiguous, because they are all touching and in the same region of the country. They view the same general area of the heart (specifically the left ventricle). What are contiguous leads in ECG? Contiguous leads are next to one another anatomically speaking.Contiguous leads are next to one another anatomically speaking.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
